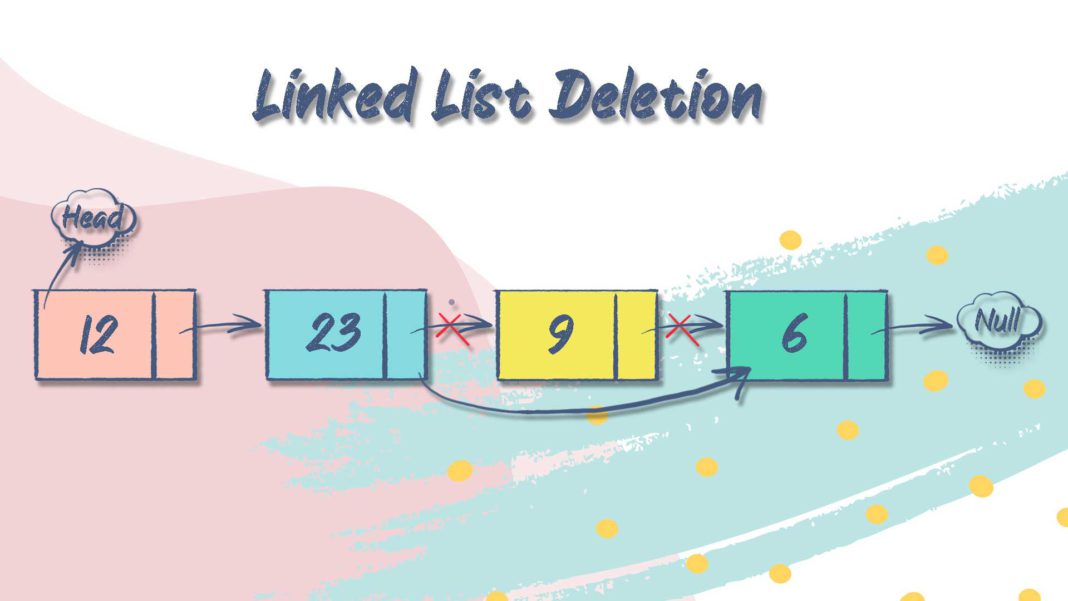
In this article, we will discuss about linked list deletion. We will see how to delete a node in a Singly linked list.
This article will be continuation of our Linked List tutorial series. You can navigate to other parts from here:
- Linked List Introduction – Linked List Tutorial series #1
- Linked List Insertion – Linked List Tutorial series #2
Agenda of this article
By the end of this article, you shall be able to delete a node at any position of a linked list.
Linked List Deletion
We may be asked to delete a node in a linked list at three different places:
- delete the first node
- delete the last node
- delete the node at a given position
Let us discuss one-by-one along with the coding examples.
1. Delete the first node
- Create a temp pointer that points to the same node as Head.
- Move head pointer to the next node and dispose the temp.
In python the temp will be garbage collected when it doesn’t have any reference.
Here’s the code to delete a node at start:
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| def delete_at_start(head): | |
| # edge case: return if head is null | |
| if not head: | |
| return None | |
| head = head.next # moving head to next node | |
| return head |
2. Delete the Last Node
- Traverse the list while maintaining previous node’s address also.
- After reaching the end of the list we will have two pointers -> one pointing to tail node, other pointing to the node before tail node.
- Update previous node’s next pointer to null
- Dispose the tail node.
Here’s the code to delete a node at end:
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| def delete_at_end(head): | |
| if not head: | |
| return None | |
| prev_node = head | |
| while prev_node.next.next: | |
| prev_node = prev_node.next | |
| prev_node.next = None | |
| return head |
3. Deleting a node at a given position
- Maintain previous node and the node to be deleted.
- Once we find the node to be deleted, point the previous node’s pointer to the next pointer of the node to be deleted.
- Dispose the current node to be deleted.
Here’s the code to delete a node at a given position:
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| def delete_at_pos(head, position): | |
| if not head: | |
| return None | |
| if position is 0: | |
| return head.next | |
| prev_node = head | |
| curr_node = head.next | |
| current_pos = 1 | |
| while curr_node and current_pos < position: | |
| current_pos += 1 | |
| prev_node = prev_node.next | |
| curr_node = curr_node.next | |
| prev_node.next = curr_node.next | |
| return head |
Now let us see the executable code of deletion of Linked list where we can call all the three functions discussed above.
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| class Node: | |
| def __init__(self, data=None): | |
| self.data = data | |
| self.next = None | |
| """ | |
| Deleting a node at start. | |
| """ | |
| def delete_at_start(head): | |
| # edge case: return if head is null | |
| if not head: | |
| return None | |
| head = head.next # moving head to next node | |
| return head | |
| """ | |
| Deleting a node at end. | |
| """ | |
| def delete_at_end(head): | |
| # edge case | |
| if not head: | |
| return None | |
| prev_node = head | |
| # traversing until current node's next is null | |
| while prev_node.next.next: | |
| prev_node = prev_node.next | |
| # deleting the reference of previous node's next | |
| prev_node.next = None | |
| return head | |
| def delete_at_pos(head, position): | |
| # edge case | |
| if not head: | |
| return None | |
| if position is 0: | |
| return head.next | |
| # maintaining previous and current nodes | |
| prev_node = head | |
| curr_node = head.next | |
| current_pos = 1 | |
| while curr_node and current_pos < position: | |
| current_pos += 1 | |
| prev_node = prev_node.next | |
| curr_node = curr_node.next | |
| prev_node.next = curr_node.next | |
| return head | |
| def insert(head, data): | |
| if not head: | |
| return Node(data) | |
| temp = Node(data) | |
| temp.next = head | |
| head = temp | |
| return head | |
| if __name__ == '__main__': | |
| # start with empty list | |
| head = None | |
| head = insert(head, 5) | |
| head = insert(head, 4) | |
| head = insert(head, 3) | |
| head = insert(head, 2) | |
| head = insert(head, 1) | |
| # delete at a given position | |
| head = delete_at_pos(head, 2) | |
| # deleting a node at start | |
| head = delete_at_start(head) | |
| # deleting a node at end | |
| head = delete_at_end(head) | |
| while head: | |
| print("{}".format(head.data), end=" ") | |
| head = head.next |
Time Complexity
Time complexity for deleting a Node is O(n) where n is the length of linked list, as worst case might be last of the node to be deleted and we need to traversing the entire list.
Space Complexity
Space complexity – O(1) for a temp variable.